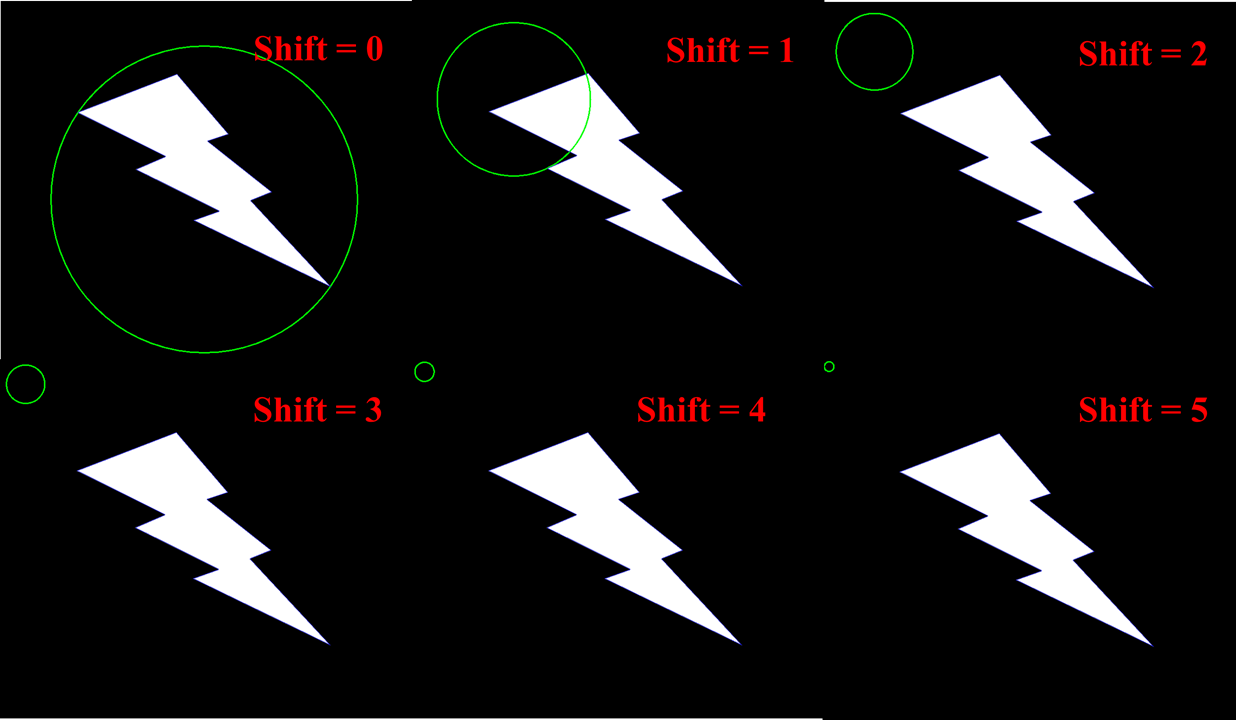
函数中的代码是部分代码,详细代码在最后
1 cv2.boundingRect
作用:矩形边框(boundingRect),用于计算图像一系列点的外部矩形边界。
cv2.boundingRect(array) -> retval
参数:
array - 灰度图像(gray-scale image)或 2D点集( 2D point set )
返回值:元组
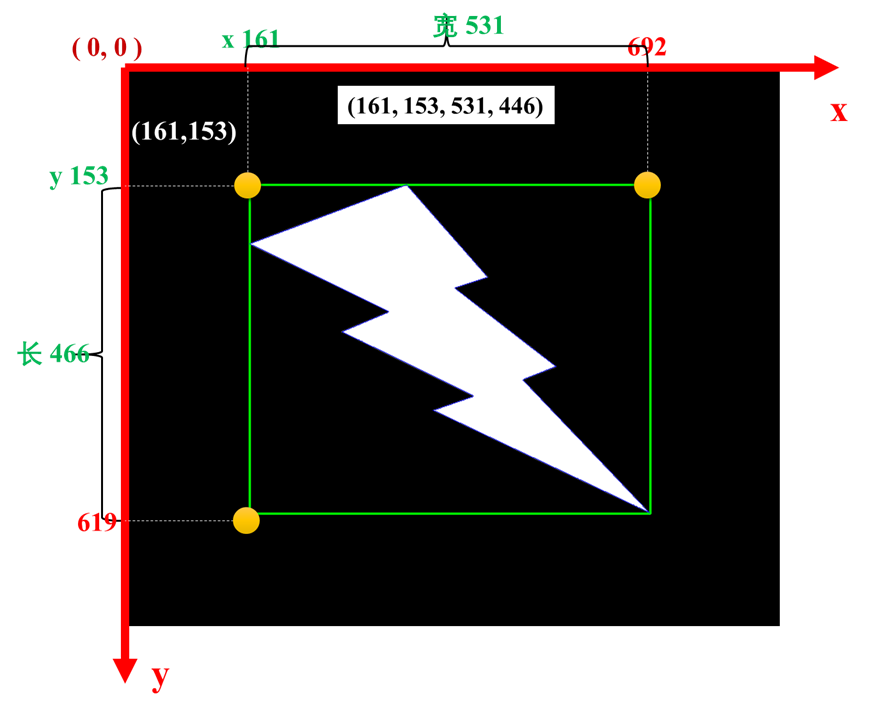
元组(x, y, w, h ) 矩形左上点坐标,w, h 是矩阵的宽、高,例如 (161, 153, 531, 446)
代码示例:
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(re_img, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)for c in contours:# find bounding box coordinates# 现计算出一个简单的边界框x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(c)# 画出矩形cv2.rectangle(img, (x,y), (x+w, y+h), (0, 255, 0), 2)
2 cv2.minAreaRect
作用:minAreaRect - min Area Rect 最小区域矩形;计算指定点集的最小区域的边界矩形,矩形可能会发生旋转 possibly rotated,以保证区域面积最小。
cv2.minAreaRect(points) -> retval
参数:
points - 2D点的矢量( vector of 2D points )
返回值:元组
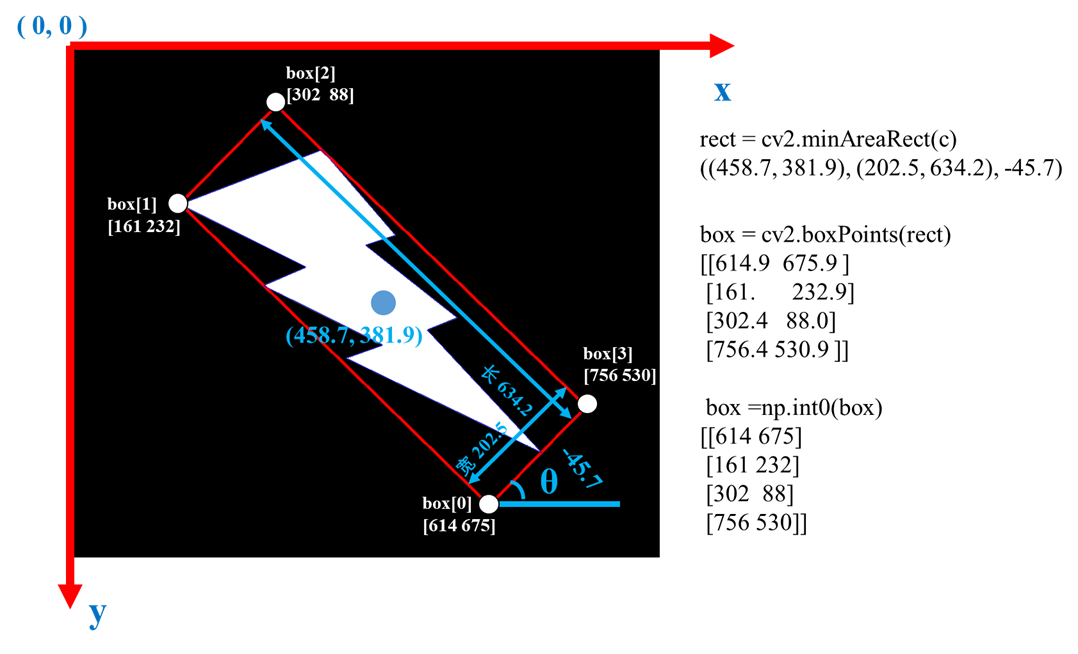
元组((最小外接矩形的中心坐标),(宽,高),旋转角度)-----> ((x, y), (w, h), θ )
关于旋转角度的注意事项:
1)旋转角度是水平轴(x轴)逆时针旋转,与碰到的矩形第一条边的夹角。
2)“ 第一条边 " 定义为 宽width,另一条边定义为高 height。这里的宽、高不是按照长短来定义的。
3)在 opencv 中,坐标系原点在图像左上角,将其延伸到整个二维空间,可以发现 “x轴镜像对称”,角度则 逆时针旋转为负、顺时针旋转为正。故θ∈(-90度,0];(笛卡尔坐标系中,逆时针为正、顺时针为负)
4)旋转角度为角度值,而非弧度制。
如 ((458.70343017578125, 381.97894287109375), (202.513916015625, 634.2526245117188), -45.707313537597656)
但绘制这个矩形,一般需要知道矩形的 4 个顶点坐标;通常是通过函数 cv2.boxPoints()获取。
2.1 附1 : cv2.boxPoints
作用:查找旋转矩形的 4 个顶点(用于绘制旋转矩形的辅助函数)。
cv2.boxPoints(box) -> points参数:
box - 旋转的矩形
返回值:列表list
points - 矩形 4 个顶点组成的列表 list
返回值示例:
[[614.9866 675.9137 ][161. 232.99997][302.4203 88.04419][756.40686 530.9579 ]]
2.2 附2:int0
int0 有两种相近的描述,
第一种,int0 意味是 64位整数。字符代码'l'。与 Python int兼容,参考文档https://kite.com/python/docs/numpy.int0
int0 ( *args, **kwargs )第二种,等价于intp,在 数组类型和类型之间的转换 文档中,有intp,释义为 “ 用于索引的整数(与C ssize_t相同;通常为int32或int64)”
有人说不建议使用int0, 因为它等同内容不完全一致,如 int32,int64.
相关参考:
locating corner position using opencv
What are np.int0 and np.uint0 supposed to be?
numpy 的 int0
数据类型 --> 数组类型和类型之间的转换
What is numpy method int0?
代码示例:
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(re_img, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)for c in contours:# find minimum area# 计算包围目标的最小矩形区域rect = cv2.minAreaRect(c)# calculate coordinate of the minimum area rectangle# 计算矩形的 4 点坐标,返回结果为float数据类型box = cv2.boxPoints(rect)# normalize coordinates to integers# 将float类型转为 int,在这里最好写成int32 / int64# 若为int0,有时候出错都不知道错在那 box =np.int0(box)# 注:OpenCV没有函数能直接从轮廓信息中计算出最小矩形顶点的坐标。所以需要计算出最小矩形区域,# 然后计算这个矩形的顶点。由于计算出来的顶点坐标是浮点型,但是所得像素的坐标值是整数(不能获取像素的一部分),# 所以需要做一个转换# draw contourscv2.drawContours(img, [box], 0, (0, 0, 255), 3) # 画出该矩形
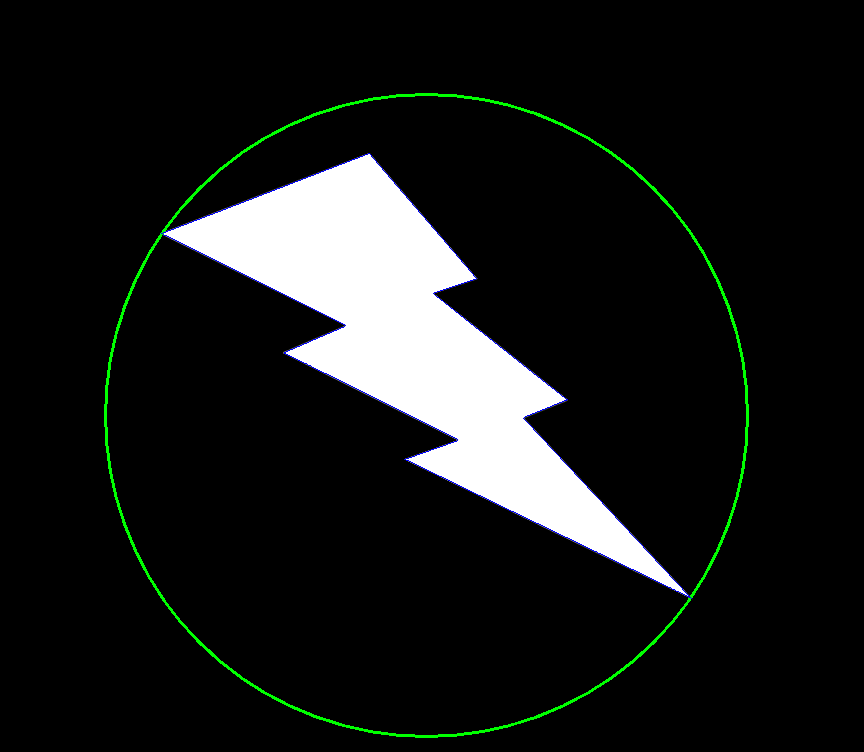
3 cv2.minEnclosingCircle
作用:使用迭代算法( iterative algorithm)查找包含2D点集的最小区域的圆(Finds a circle of the minimum area enclosing a 2D point set)。
cv2.minEnclosingCircle(points) -> center, radius
参数:
points - 2D点矢量(vector of 2D points)
返回值:
center - 圆心 (x, y)
radius - 半径 r
如:((426.0, 415.5), 321.7628173828125)
代码示例:
# calculate center and radius of minimum enclosing circle # 会返回一个二元组, # 第一个元素为圆心的坐标组成的元组,第二个元素为圆的半径值。 (x, y), radius = cv2.minEnclosingCircle(c) # 转为整数 cast to integers center = (int(x), int(y)) radius = int(radius) # 绘圆 draw the circle img = cv2.circle(img, center, radius, (0, 255, 0), 2)
或者
cen, rad = cv2.minEnclosingCircle(c) cen = tuple(np.int0(cen)) rad = np.int32(rad) img = cv2.circle(img, cen, rad, (0, 255, 0), 2)
运行

注意:
cv2.circle() 函数使用时,圆心参数不能是数列array,必须是元组tuple
绘制圆cv2.circle() 函数的使用方法。
3.1 附1:cv.circle()
作用:画圆环或实心圆
cv2.circle(img, center, radius, color[, thickness[, lineType[, shift]]]) -> img参数:
img - 目标图像
center - int 圆心,必须是元组tuple形式、不能是列表 list,必须是整型int、不能是浮点型float;
radius - int 半径,必须是整型int、不接受浮点型float。
color - 圆的颜色
thickness - int thickness = 1 圆轮廓的厚度(正数 positive),若为负值(Negative values),意味全填充的实心圆。
lineType - int lineType = 8 圆轮廓的线性,
- 8 (or omitted) - 8-connected line.
- 4 - 4-connected line.
- CV_AA - antialiased line.
shift - int shift = 0 help帮助文档直译 圆心、半径值的小数位(Number of fractional bits in the coordinates of the center and in the radius value),事实上,当执行代码时,貌似又不是这个意思 。
以上若不是整数int,则会报错 TypeError: integer argument expected, got float
示例代码如下
(x, y), radius = cv2.minEnclosingCircle(c) center = (int(x), int(y)) radius = int(radius) img = cv2.circle(img, center, radius, (0, 255, 0), thickness=2,lineType=8,# shift=0)# shift=1)# shift=2)# shift=3)# shift=4)# shift=5)shift=6)分别运行,其结果:
需要注意的是不同的图,其运行代码后的识别效果是不同的,我当时用 ppt 制备 闪电 lighning 时并没有在意图片格式,就造成了运行代码后的识别结果与别人的不一致,后来将图片保存成黑底白图,和别人的图像一致了。

说明:
1)在运行代码时图片没有红色边框,为了说明每一个图,后加上的红色图像边框。
2)a、b图的大小不一样,其运行后识别的结果不一样。
3)b、d图的背底和图案颜色正好相反,其由于函数 cv2.threshold()的参数一致,所以其结果也不一致。
4)c、d图的是有无背底,其运行后识别结果也有所区别。
以上只是说明同一个代码,针对图的稍微差别,其识别结果也会存在差别。以后注意这方面内容就行。暂不深究。
4 cv2.rectangle
作用:绘制一个矩形轮廓或一个填充矩形。
cv2.rectangle(img, pt1, pt2, color[, thickness[, lineType[, shift]]]) -> img
参数:
img - 待rectangle函数处理的图像
pt1 - 矩形的顶点
pt2 - 矩形的另一个顶点(但该顶点与pt2顶点相对)
color - 矩形的颜色或亮度(灰度图像)
thickness - 矩形边框的粗细,若为负值,则矩形为全填充的。int thickness=1。
lineType - Type of the line. See #LineTypes。int lineType=8。
shift - Number of fractional bits in the point coordinates.。int shift=0。
返回值:
img - 被rectangle处理过的图像。
该函数还可以直接输入矩形来替代pt1、pt2 对角点,代码如下:
cv2.rectangle(img, rec, color[, thickness[, lineType[, shift]]]) -> img
参数:
rec - 矩形,
代码示例:
# 计算出一个简单的边界框, # 参数c为图像轮廓findContours返回值 x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(c) # 绘制矩形 # 将轮廓信息转换成(x, y)坐标,并加上矩形的高度和宽度 cv2.rectangle(img, (x,y), (x+w, y+h), (0, 255, 0), 2)
运行结果:

5 全代码分析
将上述函数中代码整理,所有的代码如下
import cv2 import numpy as npimg = cv2.imread('lightning.png',cv2.IMREAD_UNCHANGED) # img = cv2.pyrUp(img) img_gray = cv2.cvtColor(img.copy(), cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)ret, re_img = cv2.threshold(img_gray, 127, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY) contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(re_img, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)for c in contours:# 查找矩形边界 find bounding box coordinates# 计算出简单的边界框,返回顶点坐标、宽、高x,y,w,h = cv2.boundingRect(c)# 它将轮廓信息转换程(x,y)坐标,并加上矩形的高度和宽度cv2.rectangle(img,(x,y),(x+w, y+h),(0,255,0),2)# find minimum area# 计算出包围目标的最小矩形区域rect = cv2.minAreaRect(c)# calculate coordinates of the minimum area rectangle# 计算矩形的 4 个坐标点,float形式box = cv2.boxPoints(rect)# normalize coordinates to integers# 将坐标值整数化box = np.int0(box)# draw contours# opencv没有函数能直接从轮廓信息中计算出最小矩形顶点的坐标。# 所以需要计算出最小矩形区域,然后计算这个矩形的顶点。# 计算出的顶点坐标都是浮点型,而所有像素的坐标值都是整数,# 所以需要做转换整数,然后画出这个矩形cv2.drawContours(img, [box], 0, (0,0,255), 3)# calculate center and radius of minimum enclosing circle# 大多数绘图函数把绘图颜色和密度thickness放在最后两个参数里# 最后检查的边界轮廓为最小闭圆# minEnclosingCircle函数返回一个二元组,# 第一个元数为圆心,第二个元素为半径(x,y), radius = cv2.minEnclosingCircle(c)# cast to integerscenter = (int(x),int(y))radius = int(radius)# draw the circleimg = cv2.circle(img,center,radius,(0,255,0),2, lineType=8, shift=6)cv2.drawContours(img,contours, -1, (255,0,0), 1) cv2.imshow("contours",img) cv2.waitKey()
运行:

参考:
轮廓特征——官网
笛卡尔坐标系
python opencv minAreaRect 生成最小外接矩形
OpenCV 中boundingRect、minAreaRect、minEnclosingCircle用法
OpenCV的基本绘图函数
openCV检测物体边缘
OpenCv学习笔记3--轮廓检测,多边形 直线 圆检测
python-opencv boundingRect使用注意
简单的验证码识别(opecv)(基于c/c++的示例代码)
opencv的一些函数——contours
opencv图像轮廓
此外还有 Opencv 图像金字塔pyrDown和pyrUp函数
【OpenCV笔记 06】OpenCV中绘制基本几何图形【矩形rectangle()、椭圆ellipse() 、圆circle() 】——基于c/c++的,但可以参考