$dp$。
这道题最关键的是这句话: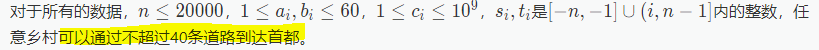
跳出思维局限大胆设状态,设$f_{x, i, j}$表示从$x$到根要经过$i$条公路,$j$条铁路的代价,那么对于一个叶子结点,有$f_{x, i, j} = c_x * (a_x + i) * (b_x + j)$,对于内部结点,有转移:
$f_{x, i, j} = min(f_{lson(x), i + 1, j} + f_{rson(x), i, j}, f_{lson(x), i, j}) + f_{rson(x), i, j + 1}$。
然后$40000 * 40 * 40$就快$512MB$了,然后最后一个点就光荣$MLE$了。
所以要写成记搜的,就可以省掉一半$f$数组的空间。
时间复杂度上界是$O(n * 40 * 40)$。
Code:


#include#include using namespace std; typedef long long ll;const int N = 20001; const int M = 41; const ll inf = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;int n, son[N][2], a[N], b[N], c[N]; ll f[N][M][M];template inline void read(T &X) {X = 0; char ch = 0; T op = 1;for(; ch > '9'|| ch < '0'; ch = getchar())if(ch == '-') op = -1;for(; ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'; ch = getchar())X = (X << 3) + (X << 1) + ch - 48;X *= op; }template inline T min(T x, T y) {return x > y ? y : x; } ll dfs(int x, int i, int j) {if(x >= n) return 1LL * c[x - n + 1] * (a[x - n + 1] + i) * (b[x - n + 1] + j);if(f[x][i][j] != inf) return f[x][i][j];return f[x][i][j] = min(dfs(son[x][0], i + 1, j) + dfs(son[x][1], i, j), dfs(son[x][0], i, j) + dfs(son[x][1], i, j + 1)); }int main() { // freopen("road20.in", "r", stdin); read(n);for(int lc, rc, i = 1; i < n; i++) {read(lc), read(rc);if(lc < 0) lc = n - 1 - lc;if(rc < 0) rc = n - 1 - rc;son[i][0] = lc, son[i][1] = rc;}for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) read(a[i]), read(b[i]), read(c[i]);memset(f, 0x3f, sizeof(f));printf("%lld ", dfs(1, 0, 0));return 0; }